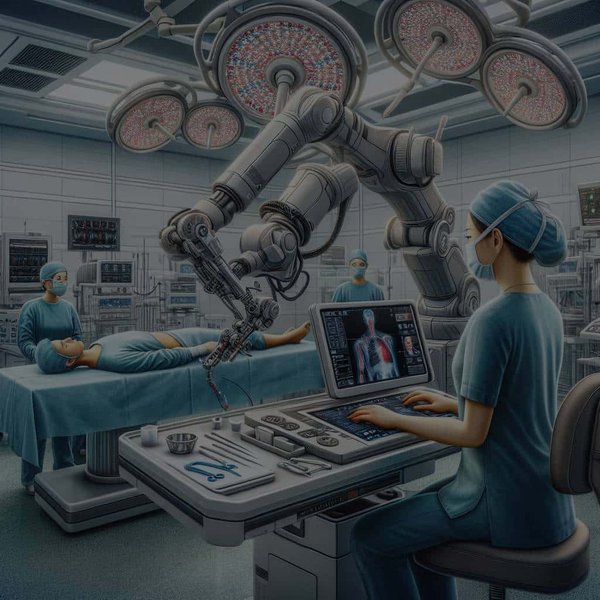
In this rapidly evolving world, technological advancements have made a significant impact on various sectors, including healthcare. Robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery is one such revolution in the medical field. From simple procedures to complex surgeries, robotic systems are becoming an integral part of the surgical landscape. Let’s delve into the emerging innovations in the realm of robotic-assisted surgery and envisage their implications on future healthcare.
The Prologue: Robotic-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery has been a game-changer in the healthcare system. It allows surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision and fewer complications. Robotic systems have taken this a step further by offering even more precision and control, making complicated surgeries safer and more efficient.
According to data from PubMed and Scholar, these systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, provide a 3D high-definition view of the patient’s body and the surgical site. They also allow surgeons to operate with enhanced stability, dexterity, and precision. As a result, patients experience less post-operative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. The question then is, what are the emerging innovations in this field, and how might they shape the future of surgical care?
The Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been making waves in the healthcare industry, transforming various aspects from diagnosis to patient care. Its integration with robotic-assisted surgery promises potential advancements that could revolutionize surgical procedures.
AI can help augment a surgeon’s capabilities by providing real-time analytics and decision-making support during surgical procedures. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze a patient’s medical history, imaging data, and other relevant information to predict potential complications and provide guidance for the best surgical approach. This not only enhances the accuracy of the surgery but also improves patient outcomes.
Also, AI-powered robots can assist in automating routine tasks, such as suturing and cutting, allowing surgeons to focus on more complex aspects of the operation. Plus, with machine learning capabilities, these robots can learn from every procedure they assist with, thereby continually improving their performance over time.
Evolution of Haptic Feedback in Robotic Systems
One of the limitations of current robotic surgical systems is the lack of tactile feedback. Surgeons rely on visual cues to assess tissue characteristics and apply appropriate force. However, the future of robotic-assisted surgery may witness enhanced haptic feedback, which will provide surgeons with a sense of touch.
Haptic feedback technology translates the feeling of pressure and resistance into a format that surgeons can interpret, helping them discern the texture and stiffness of tissues. This technology can be critical in certain procedures where the sense of touch is paramount, such as in neurosurgery or delicate manipulations in pediatric surgery. By combining haptic feedback with AI’s predictive capabilities, surgeons can potentially avoid damaging delicate structures and enhance patient safety.
The Advent of Microbots in Surgical Procedures
Imagine a swarm of tiny robots navigating through a patient’s body, performing precise surgeries without incisions. Sounds like science fiction? Not anymore. Microbots, miniature robots, are an emerging innovation set to reshape the landscape of minimally invasive surgery.
These microscopic robots can be guided through the body’s fluids to reach and operate in areas inaccessible by standard surgical tools. They are designed to perform a variety of tasks, including targeted drug delivery, blood clot removal, and even tissue biopsies. This technology could significantly reduce the invasiveness and risks associated with traditional surgical procedures.
The Promise of Tele-Surgery
Tele-surgery, also known as remote surgery, is an advanced application of robotic-assisted surgery that enables surgeons to operate on patients who are geographically distant. This is made possible through high-speed, low-latency communication networks that allow data transmission in real-time.
With advancements in 5G technology, tele-surgery can overcome latency issues that previously posed challenges. This can significantly improve access to specialized surgical care in remote areas or in situations where patient transport is risky or impractical.
In conclusion, the innovations in robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery promise an exciting future for healthcare. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undeniably revolutionize surgical care, making it safer, more precise, and accessible to all. Despite certain challenges, such as cost and learning curve for surgeons, the benefits they offer to patient care make them a promising prospect for the future of surgery.
Advancements in Robotic-Assisted Training for Surgeons
As the realm of robotic-assisted surgery expands, so does the need for proper training for surgeons. Traditional surgical training methods, such as cadaveric and live animal models, have several limitations, including ethical issues, cost, and lack of repeatability. Robotic surgical simulations are emerging as a potential solution to these challenges, offering a safe and efficient platform for surgeons to practice and enhance their skills.
Robotic surgical simulators, often powered by artificial intelligence, allow surgeons to practice surgical procedures in a virtual environment that closely mirrors real-life scenarios. With haptic feedback technology integrated into these simulators, surgeons can gain a realistic sense of touch, enabling them to better understand the textures and resistance of different tissues.
Moreover, these simulators can provide real-time feedback and analytics, helping surgeons learn from their mistakes and improve their performance. They can also incorporate machine learning algorithms to adapt to the surgeon’s skill level and customize the training modules.
Furthermore, with advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), robotic surgical training is becoming increasingly immersive and interactive. Surgeons can use VR headsets to get a 360-degree view of the surgical site and superimpose virtual images onto real-world views with AR for enhanced visualization.
Despite the initial set-up cost, robotic surgical simulators can prove to be cost-effective in the long run by reducing the time required for training and the chances of surgical errors. PubMed Google and Google Scholar have numerous studies corroborating the efficacy of these simulators in improving surgeons’ proficiency and patient outcomes.
The Future of Robotic-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
Robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery has come a long way since its inception. With the integration of artificial intelligence, haptic feedback, microbots, and tele-surgery, it is bound to transform the landscape of healthcare.
However, we are just scratching the surface. The future of robotic-assisted surgery lies in continuous innovation and exploration of uncharted territories. For instance, combining nanotechnology with microbots could lead to nanobots capable of performing cellular-level surgeries. Similarly, the integration of quantum computing with artificial intelligence could significantly improve data processing speed and accuracy, leading to better surgical outcomes.
While the potential of these technologies is immense, they also pose new challenges and ethical considerations. The high cost of robotic systems could exacerbate health care disparities, and the reliance on AI could raise issues related to accountability and data privacy. It is crucial to address these concerns while advancing these technologies to ensure they are accessible and beneficial to all.
In conclusion, the future of robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery holds immense promise. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will revolutionize surgical care, reducing surgical complications, enhancing patient outcomes, and making surgical care more accessible. As we step into this exciting new era of healthcare, the key lies in harnessing these advancements while ensuring ethical and equitable distribution.